Edificio PO
Edificio de vivienda colectiva, Soria
Collective Housing Block, Soria
Arquitectura/Architecture Estudio Juarranz, Angela Juarranz, José Ángel Juarranz
Promotor/Developer Privado
Construcción/Construction Construcciones Llorente Izquierdo S.L.
Fotografía/Photographs Estudio Juarranz
Lugar/Location Soria
Año/Year 2023
Edificio de vivienda colectiva, Soria
Collective Housing Block, Soria
Arquitectura/Architecture Estudio Juarranz, Angela Juarranz, José Ángel Juarranz
Promotor/Developer Privado
Construcción/Construction Construcciones Llorente Izquierdo S.L.
Fotografía/Photographs Estudio Juarranz
Lugar/Location Soria
Año/Year 2023
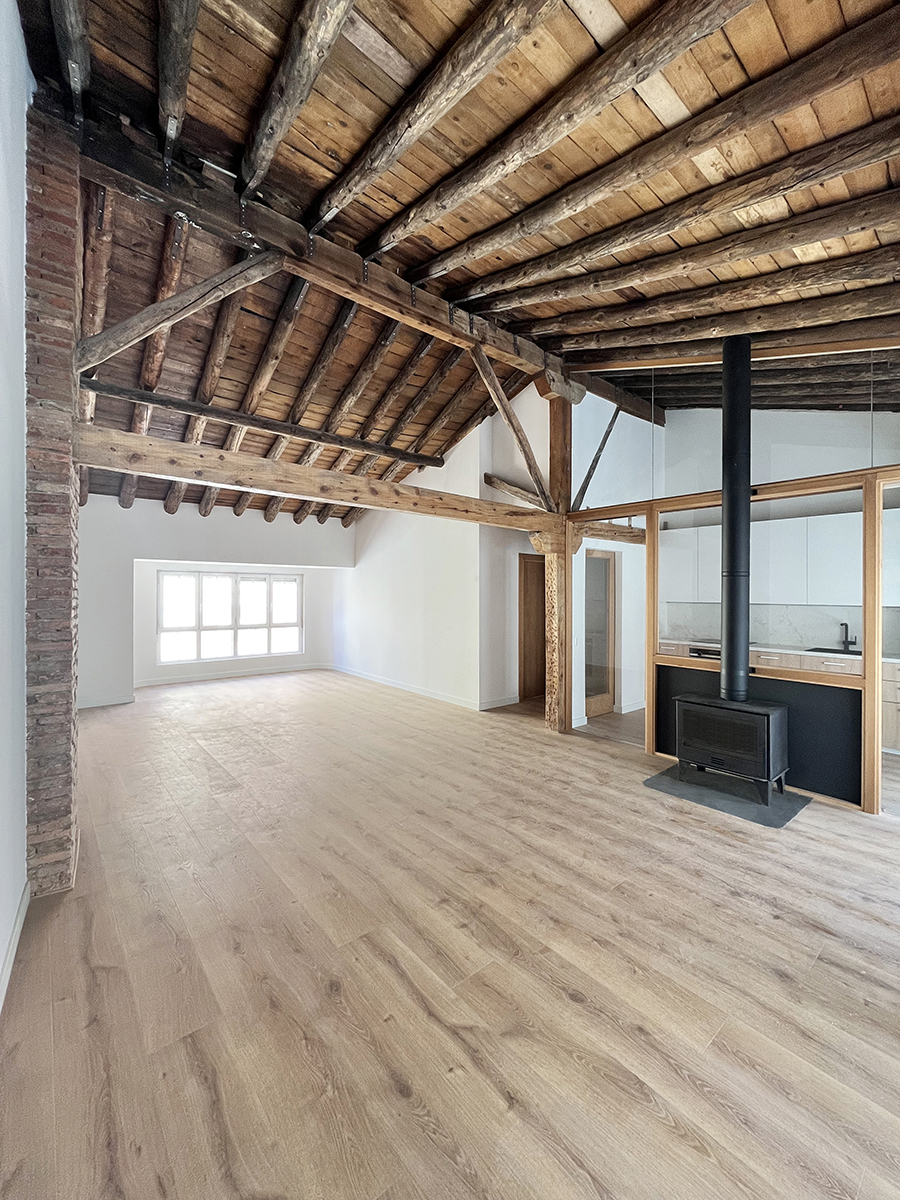
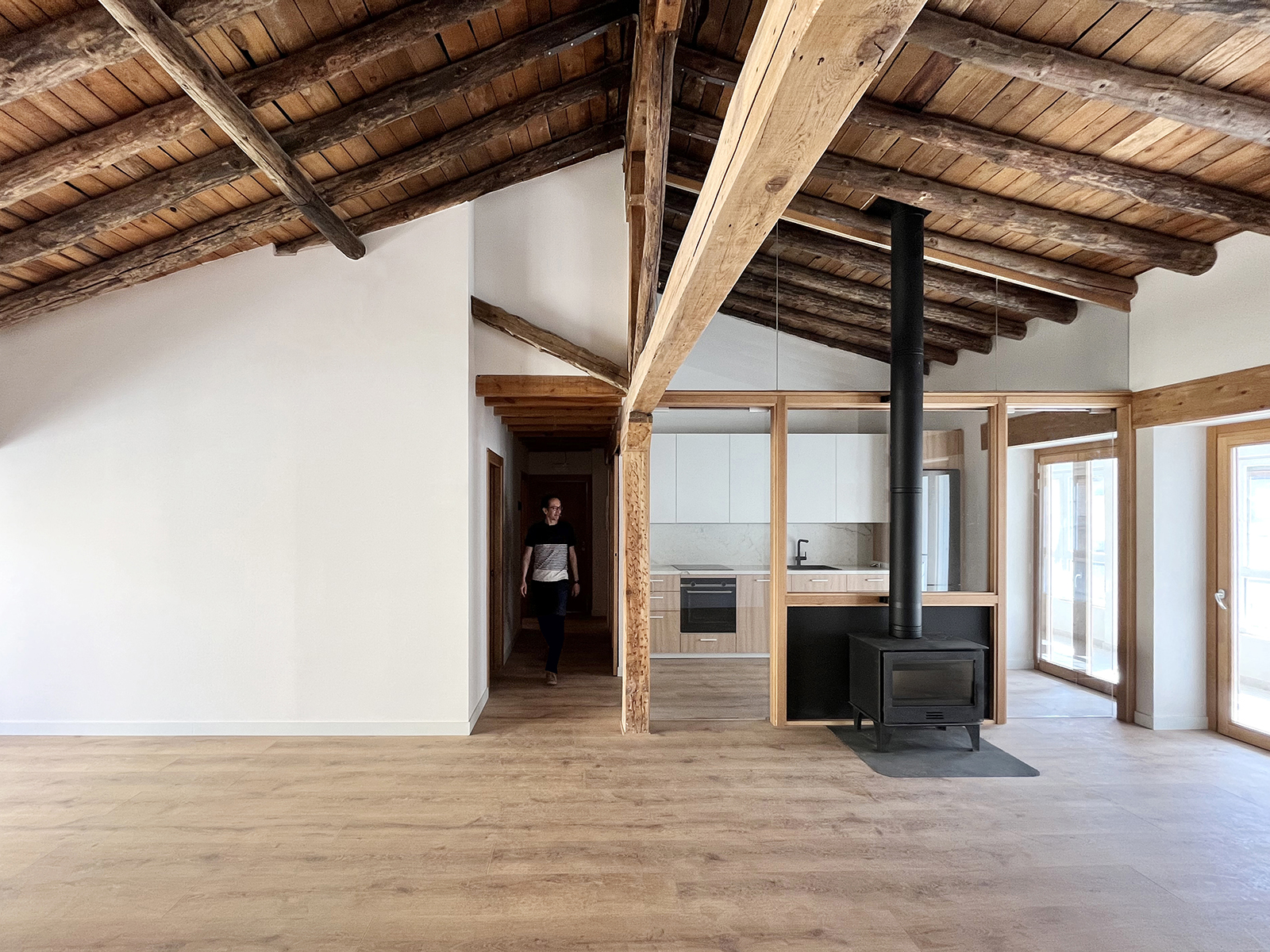
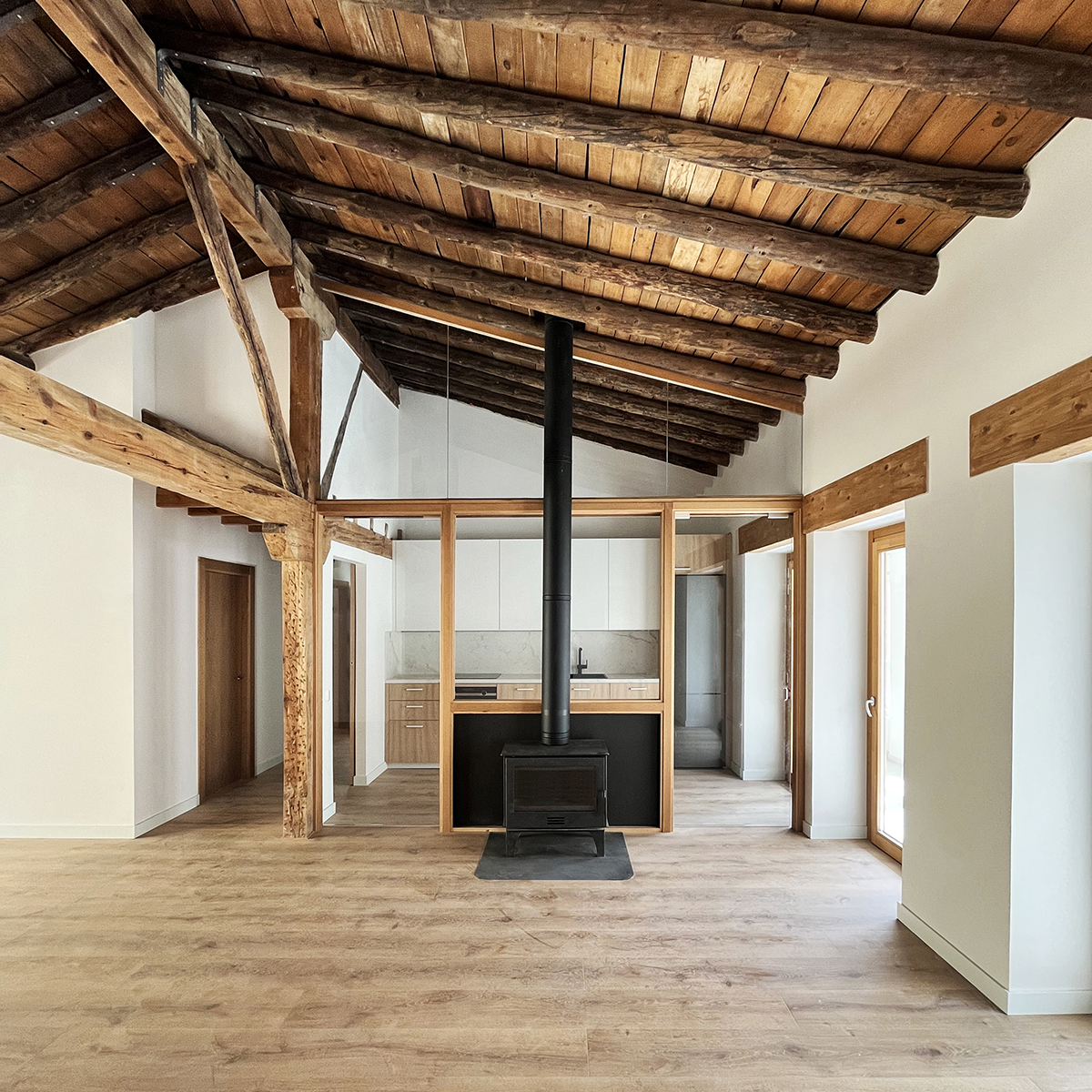
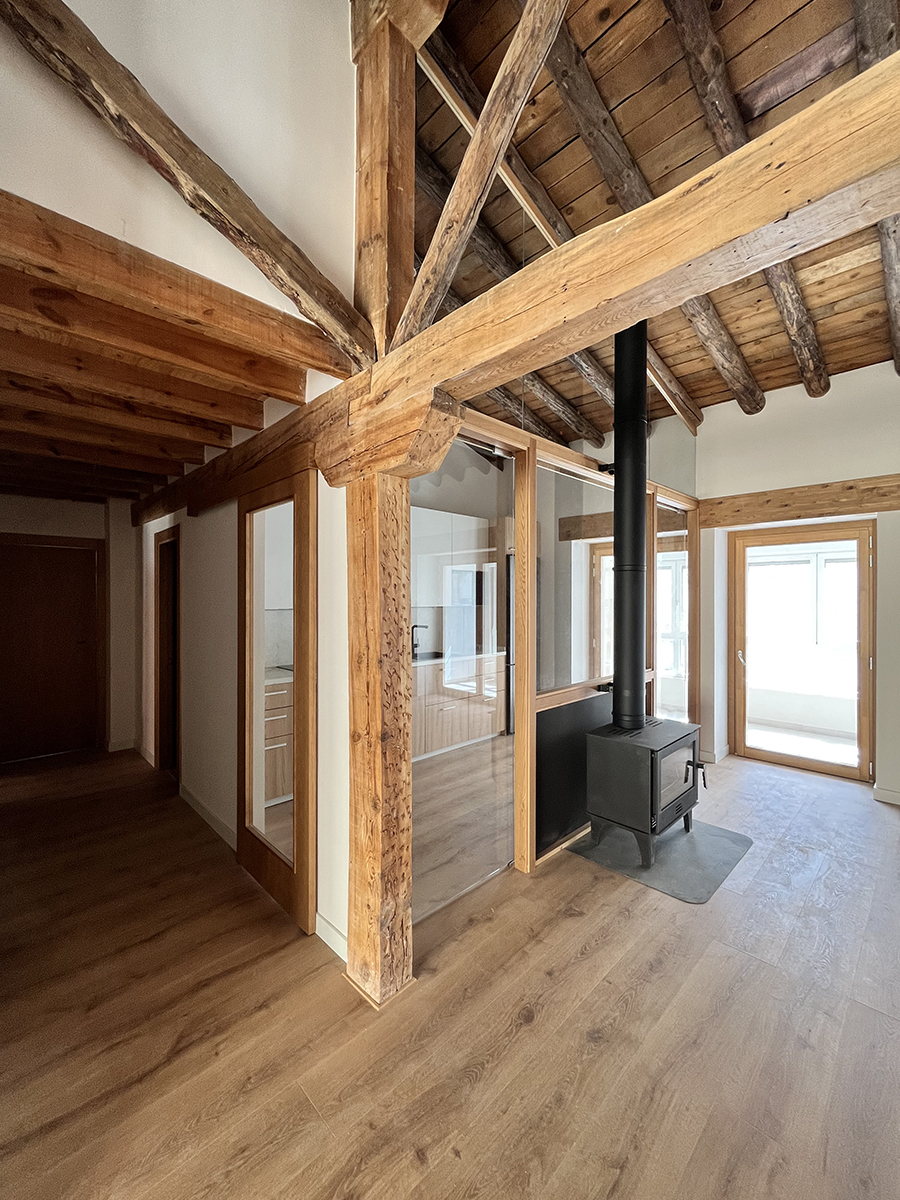










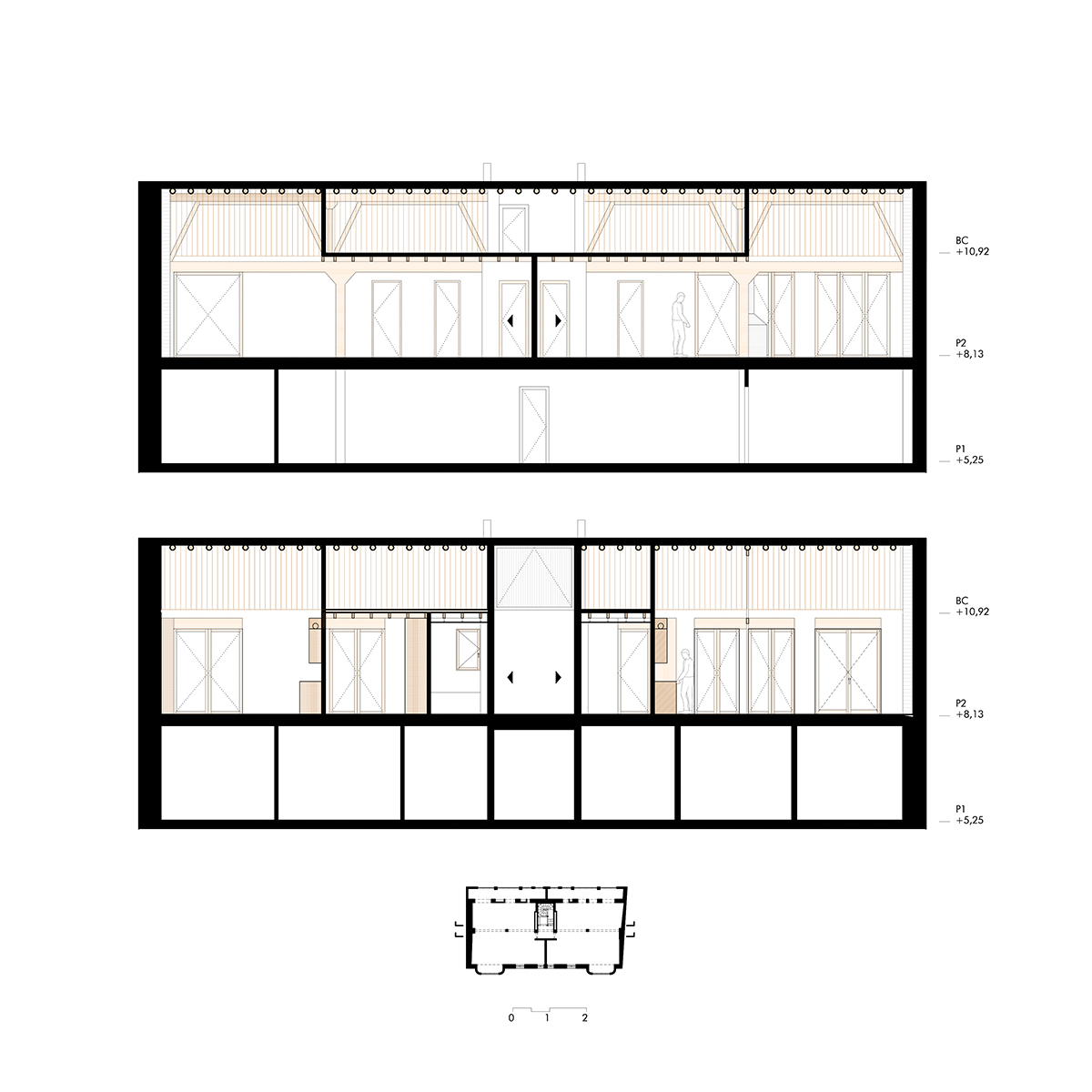
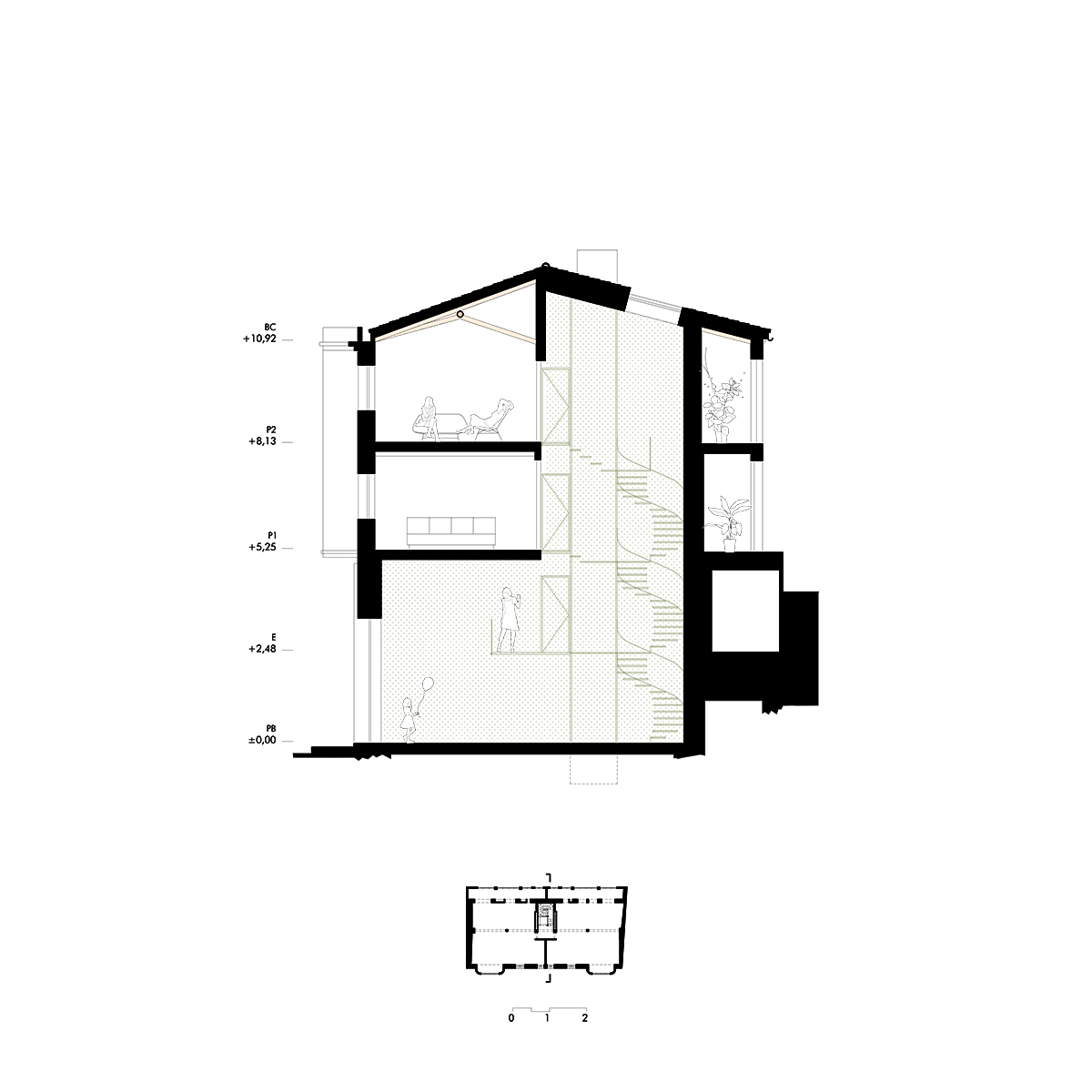
Escenario doméstico
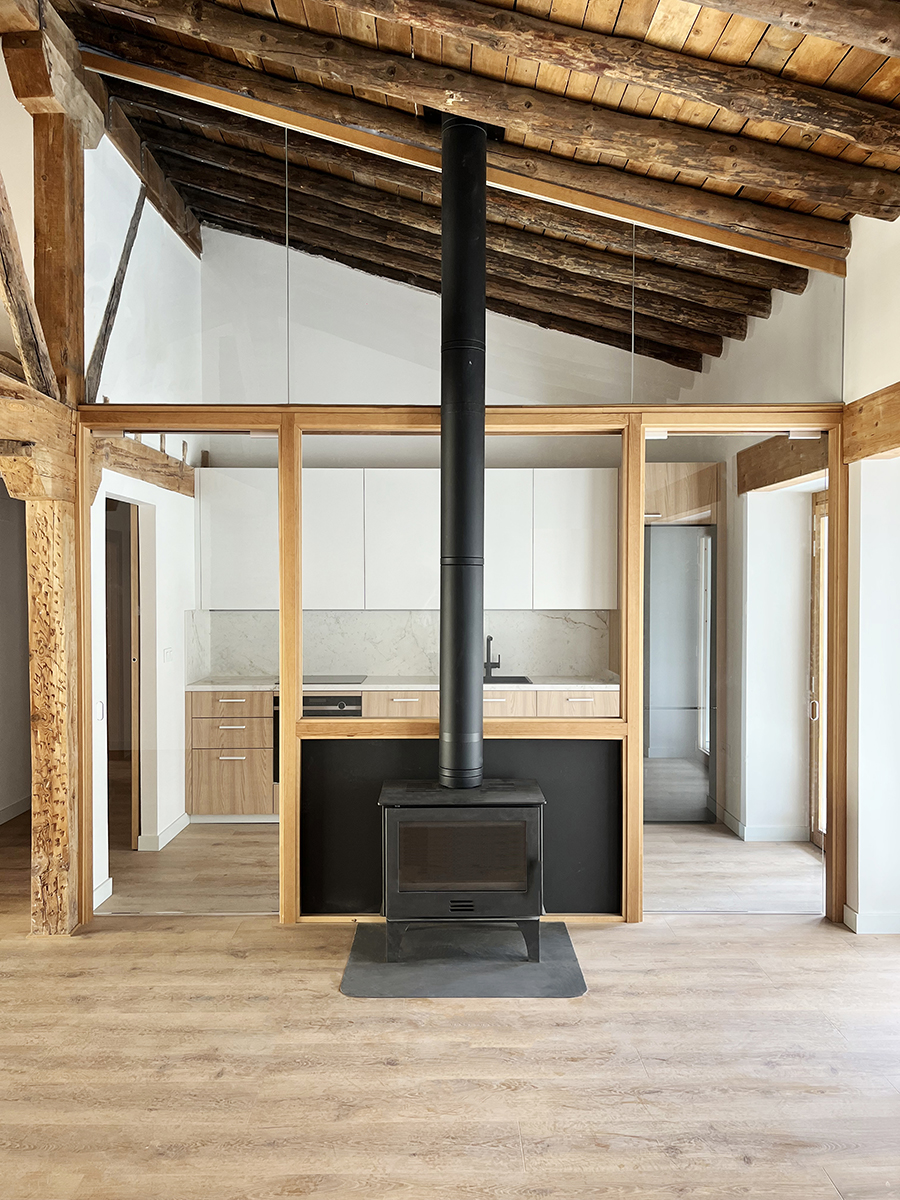
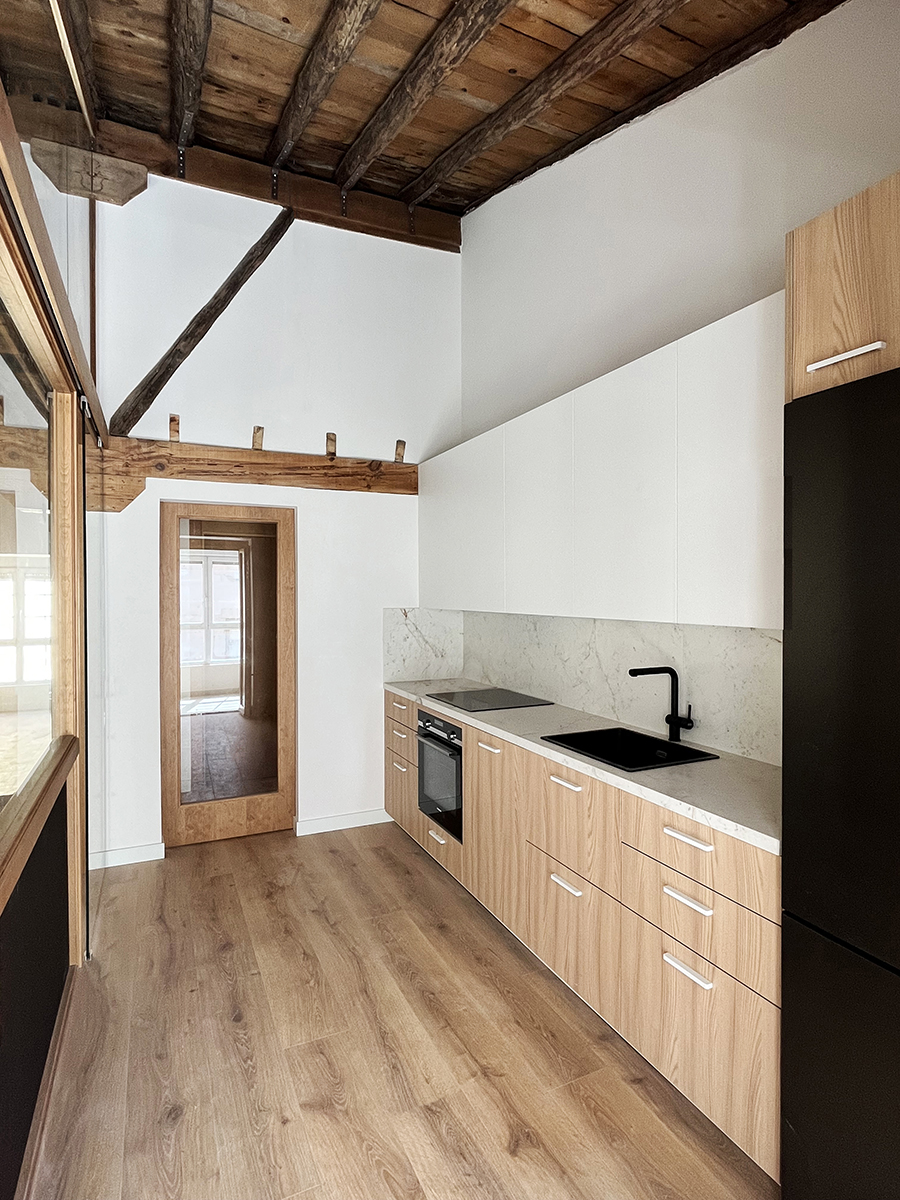
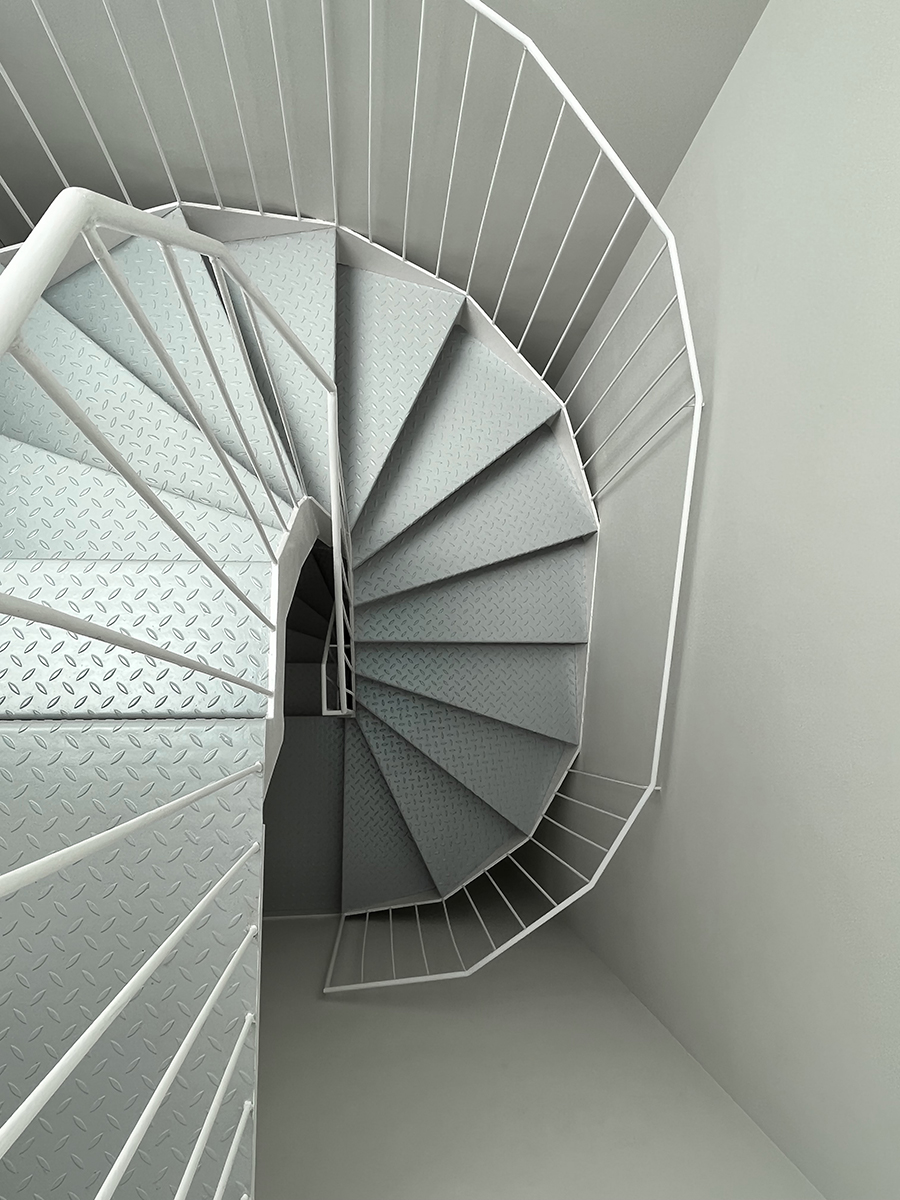
La rehabilitación de arquitecturas obsoletas o deterioradas presenta una oportunidad de actualización a diferentes niveles, como son el funcional, el estructural o el energético. La renovación de este edificio residencial incide en estos tres factores y lo hace desde la escala general hasta la escala de las viviendas. En cuanto al alcance global, la transformación de las zonas comunes se basa en la mejora de la espacialidad y la funcionalidad mediante la apertura de forjados intermedios, la incorporación de un gran lucernario y la instalación de un nuevo núcleo vertical con ascensor. La transformación de las viviendas ofrece nuevas posibilidades para habitar y disfrutar el espacio doméstico acorde a las dinámicas contemporáneas. Entre las principales estrategias destaca la continuidad y conexión de las zonas más públicas de la vivienda, en un juego espacial que también posibilita la independencia puntual de dichas estancias.
Rehabilitación estructural
La rehabilitación del edificio permite descubrir un interesante armazón de madera aserrada oculto hasta ahora. Para su actualización, por un lado, se eliminan aquellos elementos que limitan la usabilidad y disfrute de la vivienda en aras de aumentar la amplitud y altura de los espacios útiles. Por otra parte, se consolida toda la estructura restante en una cuidada operación que incorpora vigas de carga de madera y uniones metálicas a medida. Junto a la rehabilitación estructural, la detección de los materiales ocultos hace énfasis en la mejora del confort y habitabilidad en los interiores domésticos, de forma que la fábrica de ladrillo y el entramado de madera constituyen la nueva atmósfera de la vivienda.
Eficiencia energética
La rehabilitación del inmueble incorpora criterios de ahorro energético y sostenibilidad para acercarse al ideal de consumo energético casi cero. Por un lado, de cara a reducir la demanda, se implementan estrategias pasivas tales como la incorporación de aislamiento, la resolución de puentes térmicos y el empleo de elementos con bajo coeficiente de transmitancia térmica. Por otro lado, las estrategias activas ayudan a minimizar el consumo al mínimo. Los paneles fotovoltaicos proporcionan electricidad para el edificio, las viviendas y las bombas de aerotemia, conectadas al ACS y el suelo radiante/refrescante.
La rehabilitación de arquitecturas obsoletas o deterioradas presenta una oportunidad de actualización a diferentes niveles, como son el funcional, el estructural o el energético. La renovación de este edificio residencial incide en estos tres factores y lo hace desde la escala general hasta la escala de las viviendas. En cuanto al alcance global, la transformación de las zonas comunes se basa en la mejora de la espacialidad y la funcionalidad mediante la apertura de forjados intermedios, la incorporación de un gran lucernario y la instalación de un nuevo núcleo vertical con ascensor. La transformación de las viviendas ofrece nuevas posibilidades para habitar y disfrutar el espacio doméstico acorde a las dinámicas contemporáneas. Entre las principales estrategias destaca la continuidad y conexión de las zonas más públicas de la vivienda, en un juego espacial que también posibilita la independencia puntual de dichas estancias.
Rehabilitación estructural
La rehabilitación del edificio permite descubrir un interesante armazón de madera aserrada oculto hasta ahora. Para su actualización, por un lado, se eliminan aquellos elementos que limitan la usabilidad y disfrute de la vivienda en aras de aumentar la amplitud y altura de los espacios útiles. Por otra parte, se consolida toda la estructura restante en una cuidada operación que incorpora vigas de carga de madera y uniones metálicas a medida. Junto a la rehabilitación estructural, la detección de los materiales ocultos hace énfasis en la mejora del confort y habitabilidad en los interiores domésticos, de forma que la fábrica de ladrillo y el entramado de madera constituyen la nueva atmósfera de la vivienda.
Eficiencia energética
La rehabilitación del inmueble incorpora criterios de ahorro energético y sostenibilidad para acercarse al ideal de consumo energético casi cero. Por un lado, de cara a reducir la demanda, se implementan estrategias pasivas tales como la incorporación de aislamiento, la resolución de puentes térmicos y el empleo de elementos con bajo coeficiente de transmitancia térmica. Por otro lado, las estrategias activas ayudan a minimizar el consumo al mínimo. Los paneles fotovoltaicos proporcionan electricidad para el edificio, las viviendas y las bombas de aerotemia, conectadas al ACS y el suelo radiante/refrescante.